|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 16 июня 2021 Дата: 16 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 294 Просмотров: 294 |
| |
Siemens Mentor Graphics Simcenter FloTHERM + FloTHERM PCB 2021.1
FloTHERM uses advanced CFD techniques to predict airflow, temperature, and heat transfer in components, boards, and complete systems, including racks and data centers. It's also the industry's best solution for integration with MCAD and EDA software. FloTHERM is the undisputed world leader for electronics thermal analysis, with a 98 percent user recommendation rating. It supports more users, application examples, libraries and published technical papers than any competing product.
FloTHERM PCB is a unique, radical software program for streamlining concept development of printed-circuit boards (PCBs), while ensuring good thermal design and accelerating the PCB design process. FloTHERM PCB facilitates collaboration between product marketing, electronic engineers and mechanical engineers on PCB design, particularly during the conceptual phase of the design process. |
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 4)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 4)
| |
|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 15 июня 2021 Дата: 15 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 389 Просмотров: 389 |
| |
ADINA v9.7.1 x64
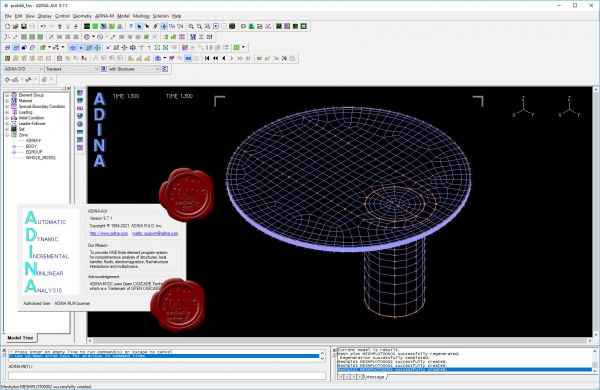
ADINA (Automatic Dynamic Incremental Nonlinear Analysis) - универсальная программа, работающая на основе метода конечных элементов, используемой для инженерных линейных и нелинейных расчётов. ADINA позволяет решать структурные и температурные задачи, рассчитывать течение, проводить мультифизические и электростатические симуляции. Внедрение программы при разработке или производстве продукта является лучшим решением для снижения затрат на производство прототипов и сокращения времени их тестирования. Современные расчётные методы, лежащие в основе программы ADINA , выгодно отличают её от остальных программ благодаря точным и надёжным результатам решения нелинейных задач.
Основные функциональные возможности пакета:
- Линейный анализ конструкций.
- Высоконелинейный анализ конструкций.
- Тепловой анализ.
- Гидродинамика.
- Взаимодействие потоков с конструкциями.
NX Nastran использует ADINA как модуль нелинейных расчетов.
Пакет ADINA состоит из следующих модулей:
- ADINA Structures - модуль расчёта статической и динамической прочности твёрдых тел и конструкций. Расчёт может быть проведён как в линейной, так и в высоконелинейной постановке с учётом нелинейности материала, больших деформаций и контакта.
- ADINA CFD – программный комплекс для моделирования течений сжимаемой и несжимаемой жидкости, использующий конечно-объемную и конечно-элементную дискретизацию.
- ADINA Thermal - программный модуль для решения задач теплопереноса в твёрдых телах и конструкциях.
- ADINA-FSI - модуль, предназначенный для анализа взаимодействия потока и конструкции, причём возможно рассмотрение высоконелинейного поведения материала вследствие больших перемещений, неупругости, контакта и температурной зависимости.
- ADINA-TMC - программный модуль, предназначенный для решения связанных термопрочностных задач, когда термические явления влияют на прочностные, и наоборот.
- ADINA User Interface (AUI) - пре- и постпроцессорный модуль, дающий возможность создавать и редактировать геометрические и конечно-элементные модели и осуществлять визуализацию результатов расчёта. Совместим со всеми модулями комплекса.
Дополнительные модули:
- ADINA Modeler (ADINA M) - встраиваемый в AUI модуль, использующий графическое ядро Parasolid и обеспечивающий твёрдотельное моделирование и прямое взаимодействие с другими CAD-системами, использующими Parasolid (Unigraphics, SolidWorks, Solid Edge)
- TRANSOR for I-DEAS, Patran - отдельный модуль, дающий возможность импортировать в ADINA и экспортировать из ADINA файлы данных в форматах I-DEAS и MSC.Patran
|
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 7)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 7)
| |
|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 13 июня 2021 Дата: 13 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 3 004 Просмотров: 3 004 |
| |
Addinsoft XLSTAT Premium 2021.2.2
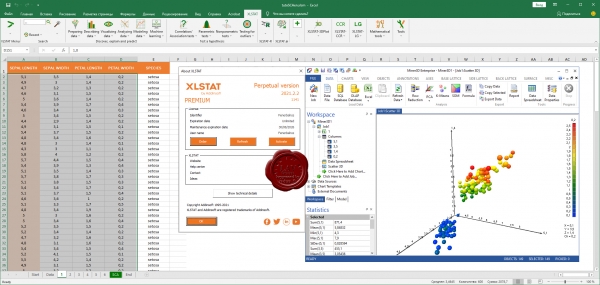
XLSTAT is a powerful yet flexible Excel data analysis add-on that allows users to analyze, customize and share results within Microsoft Excel. With over 240 standard to advanced statistical features available, XLSTAT is the preferred tool for statistical analysis in businesses and universities, large and small, and for 100,000+ users in over 120 countries across the world.
|
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 23)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 23)
| |
|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 11 июня 2021 Дата: 11 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 7 604 Просмотров: 7 604 |
| |
ESRI ArcGIS Desktop v10.8.1 + Extensions
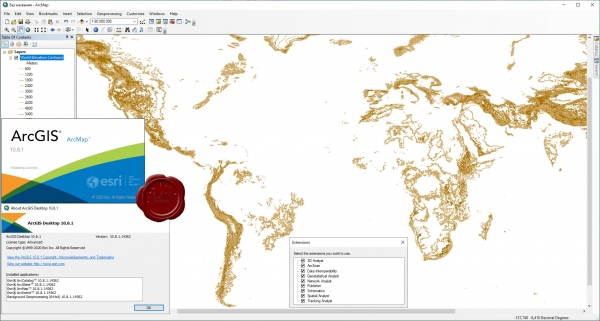
ESRI – американская компания, производитель геоинформационных систем. Семейство программных продуктов компании ArcGIS получило широкое распространение в мире и, в частности, в России. По некоторым оценкам, её доля на международном рынке ГИС составляет около 35%.
ArcGIS Desktop - настольная геоинформационная система, обладающая максимальной функциональностью в линейке программных продуктов ArcGIS. Включает всю функциональность ArcGIS for Desktop Basic (ArcView) и ArcGIS for Desktop Standard (ArcEditor) и расширяется дополнительными инструментами пространственного анализа и обработки данных, а также профессиональными картографическими инструментами. В мире геоинформационных систем ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced (ArcInfo) 'де факто' является стандартом ГИС и каждый день используется в тысячах организаций для создания, редактирования и анализа данных. |
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 31)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 31)
| |
|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 7 июня 2021 Дата: 7 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 6 052 Просмотров: 6 052 |
| |
Ensoft Suite 2021.06
APILE 2019.9.9, APILE Offshore 2019.9.9, DynaMat 2018.3.2, DYNA-N v3.0.13, DynaPile 2016.3.2,
EnCPT 2019.1.3, EnFEM 2019.1.1, GeoMat 2014.2.2, Group 2019.11.10, LPile 2019.11.9, PYWall 2019.6.9,
SETOFF 2020.4.2, SHAFT 2017.8.11, StablPro 2015.4.5, TZPILE 2021.4.1
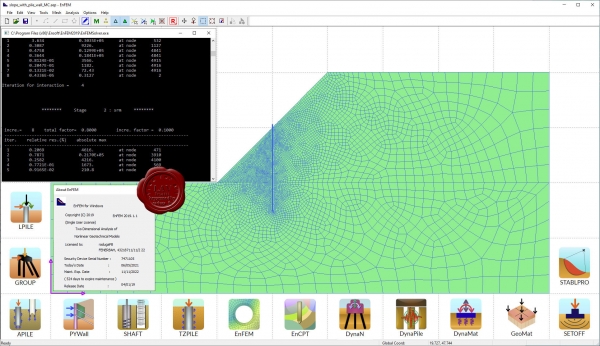
LPILE - Analyze response of piles and shafts in multi-layered soil media.
APILE - Analyze the axial capacity of driven piles in mutli-layered soils.
GROUP - Analyze response of pile groups in multi-layered soil media.
PYWall - Analyze flexible retaining walls in layered soils.
SHAFT - Study the response of drilled shafts under axial loading.
TZPILE - Analyze load-settlement relationships of vertically loaded piles with downdrag.
EnFEM - 2D finite element analysis with ability to perform soil-structure interaction and stage construction.
EnCPT - Process raw CPT data, generating and exporting soil layering and properties to LPILE.
DynaN - Determine the dynamic response of shallow and deep foundations.
DynaPile - Analyze the dynamic response of pile groups in horizontally layered elastic media.
DynaMat - Analyze the dynamic response of mat foundations under dynamic loading.
GeoMat - Analyze mat or structural slabs supported on soil media.
SETOFF - Software for computing foundation settlement.
STABLPRO - Software for computing the slope stability. |
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 39)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 39)
| |
|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 6 июня 2021 Дата: 6 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 577 Просмотров: 577 |
| |
ACI Services eRCM Pro v1.6.0.0
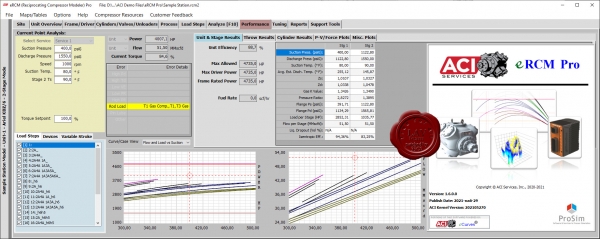
eRCM Pro replaces the highly successful eRCM Reciprocating Compressor Modeling Software, which enjoyed a twenty-year journey of helping end users model, tune, reapply, and configure their reciprocating compressors.
With so many compressors, so many performance methods, so many PLC implementations and so many restrictions for safe use, ACI’s eRCM Modeling Software provides the ideal solution to model compressor performance.
Simply specify the compressor’s geometry (frame, cylinder, stage, throw, valving, etc.) via direct inputs or by importing data from OEM software, and eRCM Pro displays that unit’s performance curves: Pressure vs. Load, Pressure vs. Flow, Pressure vs. Pressure and more, including graphs of net rod load forces, PV/PT cards, Torque Effort, and more.
Operating conditions change. Will adding a 500 in³ clearance pocket to a cylinder’s head end give enough unloading to accommodate the new operating map? Within seconds you’ll have your answer via eRCM Pro.
Tired of Gas Control using one method to predict unit performance, while engineers use another, and the PLC/operators are using yet another method to actually control the hardware? eRCM provides one methodology for disciplines within your company.
Want to see if the packager’s unloading sequence can be improved? With eRCM Pro you can easily check any combination of volume pockets and end deactivation. Including adding spacers to increase fixed clearances or adding filler pieces to volume pockets to decrease additional clearances. You can even check safety at Start Up, and check safety if certain valves fail.
No compressor performance program would be complete without the ability to improve your models. eRCM Pro does just this. Enter valid analyzer data in the tuning section, and eRCM Pro will auto-adapt the performance predictions to accommodate the real-world effects of pulsation, actual valve and parasitic losses, friction losses, etc.
eRCM Pro features:
- Model entire stations
- Manage previous versions of your models
- Fully International aware interface
- Impressive list of Units of Measure
- Advanced thermodynamic calculations using ProSim now included – full support for 400 gases with liquid dropouts
- Still, the fastest performance and graphs in the industry!
- As you expect with eRCM, fully dynamic compressor performance, PV cards, Force Plots, Torque Effort Plots, etc.
- Advanced support for Side Streams and Gas Mixing
- Improved valve modeling
- Improved gas preheat modeling
- Improved Load Step Sequence creation
- Full tables, curves, and 3D plot generation
- Support for Clearance devices, End Deactivation devices, Timed-valve Closing devices, Gas Stepless devices, and even variable stroke devices
|
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 5)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 5)
| |
|
 |
 Автор: Williams Автор: Williams
 Дата: 5 июня 2021 Дата: 5 июня 2021
 Просмотров: 516 Просмотров: 516 |
| |
ACI Services eRCM Thermodynamics v1.3.2.0
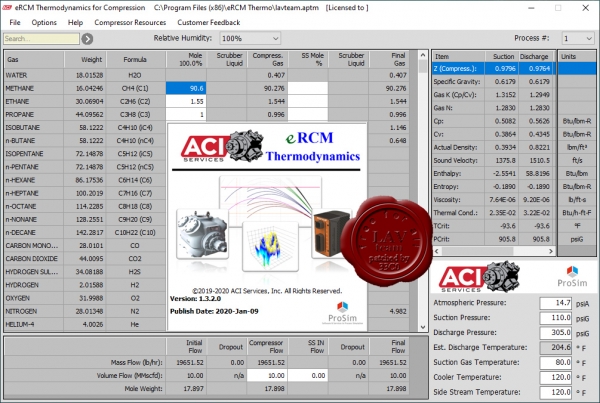
Calculating accurate compressor performance requires accurate thermodynamics. eRCM Thermo integrates ProSim’s Simulis Thermodynamics, allowing gas mixture modeling from nearly 400 individual gas components.
Once a gas/gas mixture is entered, eRCM Thermo dynamically calculates: Gas K (via CP/CV), Gas K (via balanced entropy), Compressibility (Z) factors, Specific Gravity and Density, Water Saturation, Hydrocarbon Liquid Dropouts, Phase envelope curves, Water drop out curves, Hydrate formation curves, Gas Mixing (e.g. from a side stream in), Speed of sound through gas, Variety of Units, And more, like Enthalpy and Entropy. |
| |
 Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 1)
Читать статью дальше (комментариев - 1)
| |
|
 |
| ПОИСК ПО САЙТУ |
 |
|
 |
| КАЛЕНДАРЬ | | |
 |
| « Октябрь 2025 » |
|---|
| Пн | Вт | Ср | Чт | Пт | Сб | Вс |
|---|
| | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
|
 | |
| |
|